


DUI offenders’ recidivism is estimated to fall in the range of 21–47% however, this estimate is largely conservative, considering that it does not include subjects who drink and drive without being re-arrested. Most people caught drinking and driving, after receiving a harsh punishment, drive again under the influence of alcohol after regaining their license. In 2016, law n.41 officially introduced the crimes of road killing and causing personal road injuries to Italy.
#Purpose of mmpi 2 professional
In Italy, the percentage of road traffic deaths involving alcohol is 25% in 2014, the most recent year for which data are available, there were 44,566 subjects found driving under the influence of alcohol (DUI), of whom 2,400 were younger than 21 years, new drivers, or professional drivers.
#Purpose of mmpi 2 license
Beirness and Davies (2007), in their study conducted in Canada using anonymous telephone interviews, showed that 11.6% of the population with a driving license (men: 78.1%) drive within 1 hour of consuming two or more alcoholic drinks. Globally, road traffic crashes are the main cause of death among those aged 15–29 years, while road traffic injuries are currently estimated to be the ninth leading cause of death across all age groups globally and are predicted to become the seventh leading cause of death by 2030” (p. According to the Global Status Report on Road Safety of the World Health Organization, “over 1.2 million people die each year on the world’s roads, with millions more sustaining serious injuries and living with long-term adverse health consequences. Comparisons with previous research are discussed and ideas for further study are generated.ĭrinking and driving, despite being harmful, is a widespread behavior with a significant impact on social policies.
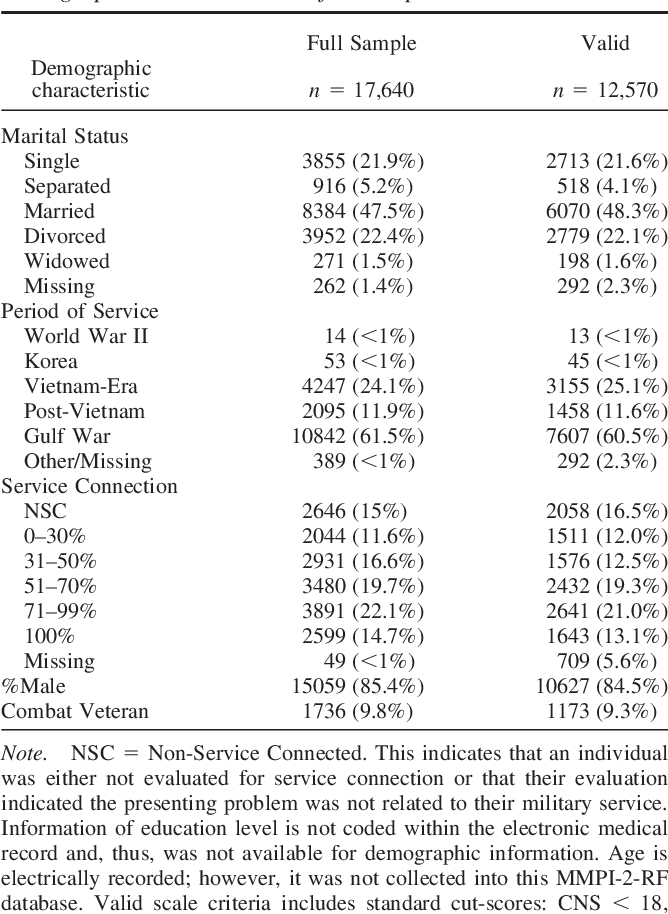
Two-step cluster analyses identified two recidivist profiles, according to 32 selected MMPI-2 validity, clinical, content, supplementary, and PSY-5 scales. The best predictors of recidivism were BAC and the scales of Lie (L), Correction (K), Psychopathic Deviate (4-Pd), Hypomania (9-Ma), and Low Self-Esteem (LSE). Results showed that, relative to DUI-NR participants, DUI-R participants had higher BAC at the time of their first conviction and more problematic MMPI-2 profiles, despite the presence of social desirability responding. A two-step cluster analysis was run to identify recidivist typologies. ANOVA and MANOVAs were performed to determine whether there were significant differences in BAC and MMPI-2 profiles between DUI-NR and DUI-R participants and a logistic regression was run to identify whether BAC at the time of the first suspension and specific personality features could predict recidivism. At the time of their first driving license suspension, participants provided their blood alcohol content (BAC) and completed a valid MMPI-2 test. The sample was comprised of 260 subjects who were not repeat DUI offenders (DUI-NR), but had a single license suspension between 20 and 97 repeat offenders who received at least two DUI convictions within a period of 5 years. The aim of this study was to identify specific risk factors and personality characteristics in repeat offenders. Many road traffic crashes are caused by Driving Under the Influence (DUI) of alcohol by persons who have previously had their license suspended for the same reason. Road traffic injuries are the ninth cause of death across all age groups, globally (WHO, 2015).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
